Wisdom Teeth
Wisdom teeth, or third molars, are the last
teeth to erupt in your mouth and are the teeth least needed for good oral
health. Most people have four wisdom teeth that usually erupt through the
gums in their late teens or early twenties. Sometimes wisdom teeth remain
trapped in the jawbone under the gums because there is insufficient room
for them to erupt.
Wisdom teeth can cause gum disease, crowding or other damage to adjacent teeth, decay (due to the inability of your toothbrush to keep the area clean), and bone destroying cysts. Pain and swelling are the most common symptoms of problem wisdom teeth. Whether you have obvious symptoms or not, it is important to diagnose existing or potential problems caused by your wisdom teeth. Removal is often the wisest decision for your health and well-being.
Wisdom teeth can cause gum disease, crowding or other damage to adjacent teeth, decay (due to the inability of your toothbrush to keep the area clean), and bone destroying cysts. Pain and swelling are the most common symptoms of problem wisdom teeth. Whether you have obvious symptoms or not, it is important to diagnose existing or potential problems caused by your wisdom teeth. Removal is often the wisest decision for your health and well-being.
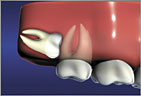 Horizontal Impaction is a severe condition that always requires extraction
Horizontal Impaction is a severe condition that always requires extraction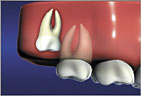 Vertically Impacted teeth may erupt, but is painful and can damage or crowd adjacent teeth
Vertically Impacted teeth may erupt, but is painful and can damage or crowd adjacent teeth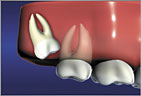 Mesial Impaction is the most common condition requiring extraction.
Mesial Impaction is the most common condition requiring extraction.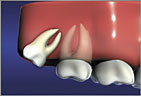 Distal Impaction is when the wisdom tooth is angled towards the rear of the mouth.
Distal Impaction is when the wisdom tooth is angled towards the rear of the mouth.